What is a Pneumatic System and How Does It Work?
A pneumatic system is an essential component in many industries. It uses compressed air to transmit and control energy. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global pneumatic systems market is expected to reach $37 billion by 2026. This growth reflects the increasing demand for automation and efficiency in manufacturing processes.
Pneumatic systems are often favored for their simplicity and reliability. They play a crucial role in various applications, such as material handling and machine operation. However, the effectiveness of these systems relies heavily on components, including compressors, valves, and actuators. Each part must work in harmony to avoid inefficiencies or failures.
Despite their advantages, pneumatic systems do face challenges. Energy loss through leaks can decrease performance. Research indicates that up to 30% of compressed air can be lost through leaks in a typical system. Addressing these issues is vital for optimizing operational costs and efficiency, pushing industries to implement better monitoring practices. As pneumatic systems evolve, the need for innovation in design and maintenance remains critical.
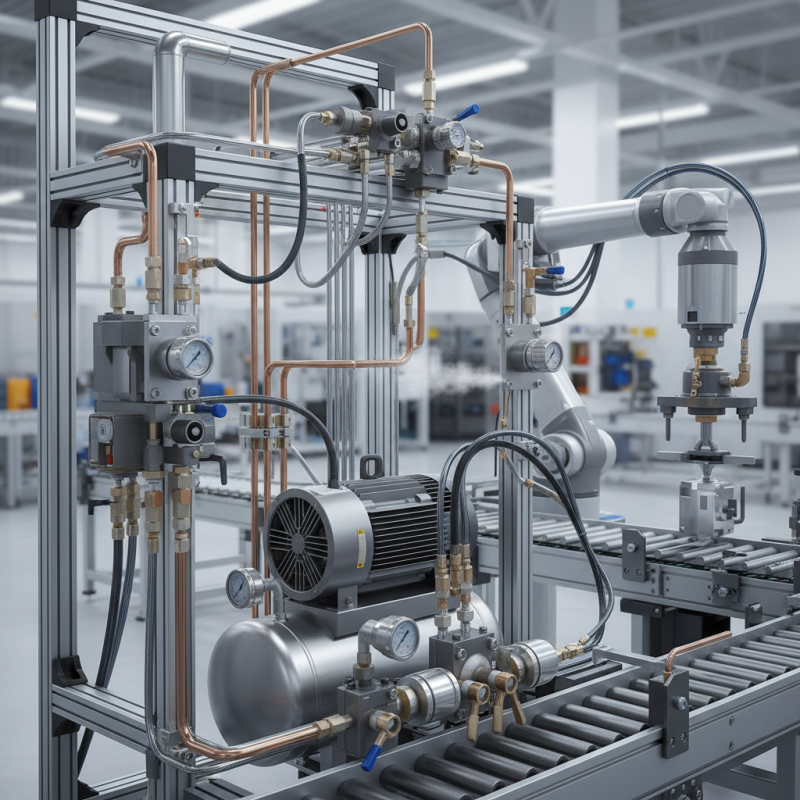

What is a Pneumatic System?
A pneumatic system uses compressed air to generate mechanical motion. It plays a significant role in various industries. The system consists of components that manage the flow of air. Common elements include compressors, valves, and cylinders. These parts work together to convert air pressure into movement.
The essential function of a pneumatic system revolves around simple principles. Compressed air is stored in tanks and distributed through pipes. When air enters a cylinder, it pushes a piston. This action creates force, enabling tools and machinery to operate. However, challenges exist. Leaks can occur in pipes, wasting energy. Maintenance is crucial to ensure efficiency.
Many users may overlook the importance of regular checks. Ignoring small issues can lead to bigger problems. It's vital to monitor air pressure and fix leaks promptly. Understanding the basic workings helps in troubleshooting common problems. A well-functioning pneumatic system can greatly increase productivity.
What is a Pneumatic System and How Does It Work?
| Component | Function | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Compressor | Generates compressed air | Reciprocating, Rotary screw |
| Air Receiver | Stores compressed air | Vertical, Horizontal tanks |
| Filters | Removes contaminants from air | Inline filters, Coalescing filters |
| Regulators | Controls air pressure | Pressure regulators, Reducing valves |
| Actuators | Converts air pressure into motion | Cylinders, Motors |
| Valves | Controls airflow in the system | Solenoid valves, Manual valves |
Basic Components of a Pneumatic System
A pneumatic system is a technology that uses compressed air to perform work. Its basic components work together seamlessly. One essential part is the air compressor. It converts electrical energy into compressed air. This air is stored in a tank. The pressure can reach significant levels.
Next, there are valves. These control the flow of air throughout the system. The valves can be manual or automatic. They play a crucial role in directing air to various tools or machinery. Actuators are another key component. They convert the energy from the compressed air into mechanical movement. Common actuators include cylinders and motors.
Finally, hoses and fittings connect all components. They must be durable and leak-proof. It’s surprising how often small leaks go unnoticed. A simple crack can lead to significant pressure drops. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure efficiency. Neglecting this aspect can result in performance issues. Understanding these components is vital for effective operation.
Principles of Pneumatic Power Generation
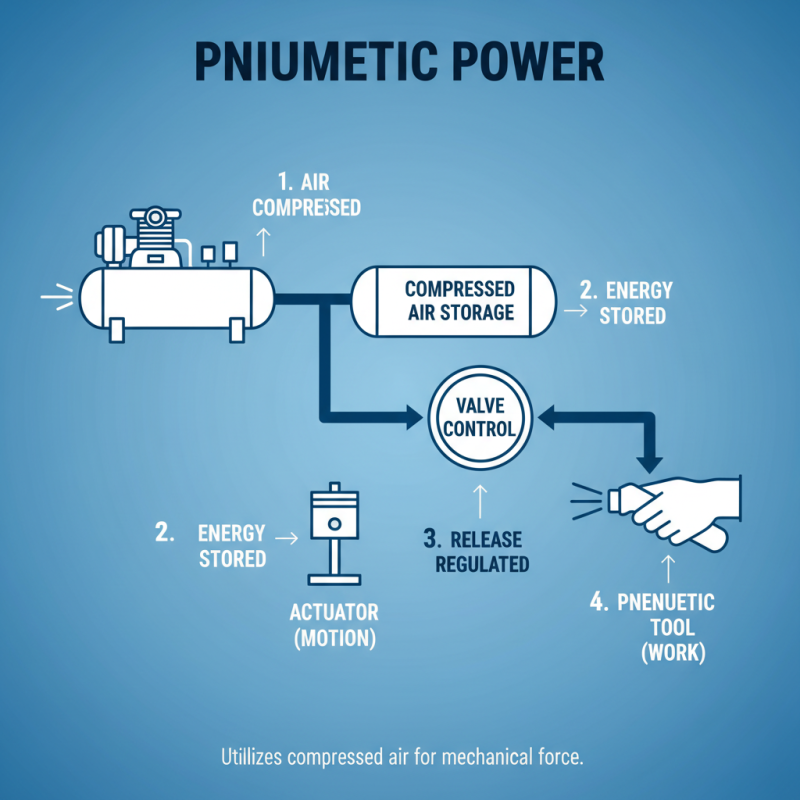
Pneumatic systems utilize compressed air to generate power. This method leverages the principles of gas behavior, particularly how air behaves under pressure. Air is compressed in a storage tank and released to perform work. Valves control this release, directing airflow to various components.
One core principle of pneumatic power generation is the relationship between pressure and volume. As air gets compressed in a smaller volume, its pressure increases. This high-pressure air can then push pistons, turn motors, or lift loads. It's efficient for tasks requiring quick, repetitive movements.
Tips for using pneumatic systems effectively include regular maintenance. Check for leaks frequently; unnoticed leaks can waste substantial energy. Ensure your air compressor is well-sized for your application, as an oversized compressor may lead to inefficiencies. Experimenting with different air pressure settings can help find the optimal balance for specific tasks. Remember, tuning your system can lead to better performance and energy savings, but finding the right setup may take time and effort.
How Pneumatic Systems Operate in Industry
Pneumatic systems play a vital role in various industries. These systems use compressed air to power tools, equipment, and processes. In factories, pneumatic systems are common due to their efficiency and speed. Workers use air-powered drills and hammers that increase productivity. These tools are often lighter than their electric counterparts, making them easier to handle.
Air compressors are essential in pneumatic systems. They increase air pressure, allowing it to flow through pipes and hoses. This pressurized air can move pistons, open valves, and activate other machinery. However, maintaining these systems can be challenging. Leaks can waste air and reduce efficiency. Regular inspections are needed to ensure optimal performance. Operators must be trained to identify signs of wear and tear.
The use of pneumatic systems isn't without drawbacks. Compressed air can be noisy, creating workplace challenges. There are also safety concerns, especially when high-pressure air is involved. If systems are not correctly maintained, they can lead to accidents. Achieving the right balance in operation is crucial. This balance ensures safety, efficiency, and productivity in industrial applications.
Advantages and Limitations of Pneumatic Systems
Pneumatic systems use compressed air for power. They are common in various applications. These systems have distinct advantages. They are generally lightweight and easy to control. Maintenance is relatively simple, too. Additionally, pneumatic systems typically have lower installation costs.
However, there are limitations to consider. The efficiency of pneumatic systems can be questionable. Compressed air may leak, leading to energy waste. This inefficiency can increase operational costs over time. Furthermore, pneumatic systems struggle with precise control compared to electrical systems. Noise levels can also be an issue. The sound of compressed air can be disruptive in certain environments.
Despite these drawbacks, pneumatic systems remain popular. Their versatility allows them to serve in multiple industries. But one must weigh the pros and cons. This careful consideration can determine the right application for pneumatic technology.
Related Posts
-
Exploring the Future of Automation: The Essential Role of Pneumatic Components in Modern Industries
-

Understanding the Role of Pneumatic Solenoids in Modern Automation Systems
-

Unlocking the Magic of Pneumatic Solenoids: A Deep Dive into Their Applications and Innovations
-

How to Choose the Right Pneumatic Air Cylinder for Your Industrial Applications
-

How to Choose the Right Norgren Valves for Your Industrial Applications 2025
-

How to Choose the Right Pneumatic Air Cylinder for Your Application
Get in Touch
570 Alden Road Unit #10, Markham Ontario Canada, L3R 8N5
Quick Links
Featured Products
Industries
