What Are Pneumatic Operated Valves and How Do They Work?
Pneumatic operated valves play a crucial role in various industries, including manufacturing and oil and gas. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global pneumatic valve market is projected to reach $8.45 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.2%. This growth underscores their importance in automating processes and enhancing efficiency.
These valves use compressed air to control fluid flow, enabling precise regulation in systems. Industries rely on pneumatic operated valves for safety and performance. However, many companies struggle to maintain these systems effectively. Regular maintenance is essential, as wear and tear can lead to failures.
Challenges remain in system integration and calibration. Many engineers find it difficult to ensure optimal performance. Addressing these issues can significantly improve reliability. Despite advancements, a gap still exists in understanding the full potential of pneumatic operated valves in automation. This calls for ongoing training and development in the field.
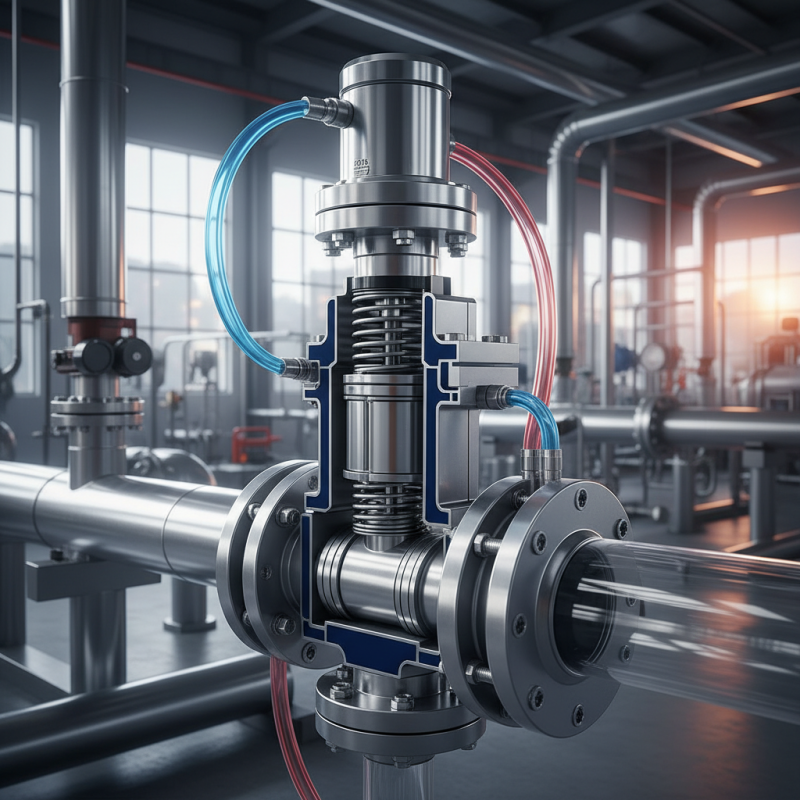
Definition and Overview of Pneumatic Operated Valves
Pneumatic operated valves are essential components in various industrial applications. These valves control fluid flow using compressed air. According to a recent industry report, the global market for pneumatic valves is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 4.5% from 2023 to 2028. This growth indicates their importance in automation and efficiency.
The working principle of a pneumatic valve involves an actuator that receives compressed air. This air pressure allows the valve to open or close. Depending on the design, these valves can be used in on/off applications or modulating flow. However, not all installations are optimal. In some cases, improper sizing or lack of maintenance can lead to inefficiencies.
Proper installation is key. A poorly calibrated valve may result in air leaks or flow restrictions. When this happens, the overall performance of a system can decline. Additionally, training personnel to understand these mechanisms is often overlooked, leading to mistakes. Awareness of the potential pitfalls can significantly enhance the effectiveness of pneumatic operated valves in any application.
What Are Pneumatic Operated Valves and How Do They Work? - Definition and Overview of Pneumatic Operated Valves
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Pneumatic Actuated Valve |
| Operation Mechanism | Controlled by compressed air to open or close the valve |
| Common Applications | Industrial processes, automation systems, and fluid control |
| Advantages | Fast response time, reduced physical wear, and ability to handle large flow rates |
| Materials Used | Aluminum, stainless steel, and various plastics |
| Control Types | On/Off control, proportional control, and fail-safe options |
| Maintenance Needs | Regular inspection and filter cleaning to prevent blockages |
| Installation Factors | Space requirements, air supply accessibility, and environmental conditions |
Key Components of Pneumatic Operated Valves
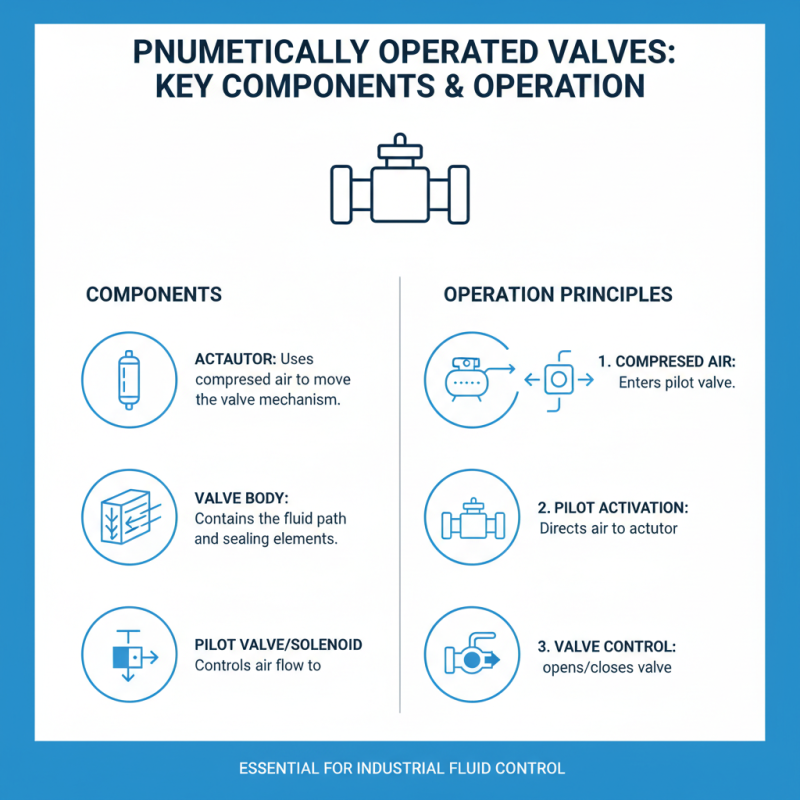
Pneumatic operated valves are essential in many industrial applications. They use compressed air to control the flow of fluids. Understanding their key components is crucial for effective operation.
One main component is the actuator. This device converts air pressure into mechanical motion. It opens or closes the valve. Check the actuator regularly. Wear and tear can lead to malfunction. A faulty actuator can cause inefficiencies in the system.
Another important part is the valve body. This encases the internal components. Materials vary based on fluid types. It’s vital to choose the right material for durability and compatibility. Improper choices may result in leaks or damage.
The control system is equally crucial. It dictates how the valve responds to signals. A poorly designed control system may mismanage operations. This can lead to unexpected flow issues or safety hazards. Refine your control setup regularly to ensure reliability.
**Tips:** Always inspect components for signs of wear. Small cracks can lead to big problems. Ensure proper air pressure levels. This keeps everything functioning smoothly. Keep a maintenance schedule to catch issues early.
Principle of Operation for Pneumatic Operated Valves
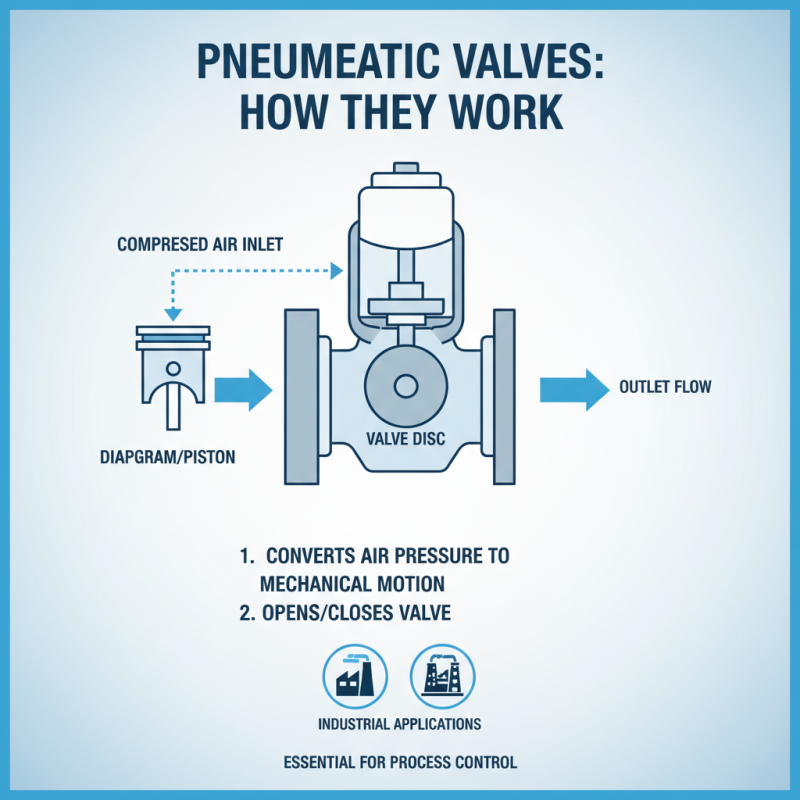
Pneumatic operated valves are essential in various industrial applications. They use compressed air to control valve movement. The principle of operation revolves around converting air pressure into mechanical motion. When the air pressure is applied, it pushes a diaphragm or piston, which opens or closes the valve.
One significant aspect is the speed of operation. According to industry reports, these valves can respond within milliseconds. This rapid response is crucial in processes that require precise control. The reliability of these valves is also noteworthy, as they tend to have lower failure rates compared to other types. Regular maintenance is vital; without it, performance can diminish.
Tips: Always check the air supply pressure. Insufficient pressure can lead to slow response times. Also, monitor for wear and tear on seals and components. Small issues can escalate if not addressed promptly. Consider having a routine check-up schedule for your pneumatic valves. This practice can prevent unexpected downtimes.
Applications of Pneumatic Operated Valves in Industries
Pneumatic operated valves have a wide range of applications across various industries. They are commonly used in manufacturing, oil and gas, and food processing. In the manufacturing sector, these valves control air pressure and flow rates. A report by MarketsandMarkets indicates that the pneumatic valve market is projected to reach $9.5 billion by 2024, growing at a CAGR of 5.2%. This growth emphasizes their importance in automation processes.
In the oil and gas industry, pneumatic valves help manage critical operations. They regulate the flow of liquids and gases during extraction and transportation, ensuring safety and efficiency. In food processing, they assist in maintaining hygiene and controlling ingredients.
Tip: Always schedule routine inspections for pneumatic valves. Small leaks can lead to significant losses. Additionally, training staff on proper usage can enhance efficiency. Understand that improper handling may lead to unplanned equipment failures. Identifying weak points in the system will help prevent issues. Emphasize a proactive approach to valve maintenance.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Pneumatic Operated Valves
Pneumatic operated valves require regular maintenance to ensure optimal functioning. They are vital for controlling air pressure systems across various industries. According to a recent report by the International Journal of Pneumatics, nearly 30% of pneumatic valve failures are due to inadequate maintenance. This statistic highlights the importance of routine checks and servicing.
Common issues include leaks, sticking valves, or erratic operation. These can often stem from worn seals or contaminated air supply. Regular inspections can catch these problems early. For example, a simple visual check can reveal signs of wear. Scheduled replacements of seals can prevent future breakdowns and costly repairs.
Troubleshooting pneumatic valves often requires a systematic approach. When a valve isn’t responding, it may not be related to the valve itself. Issues could arise from the air compressor or associated piping. A thorough examination helps identify the root cause. According to industry surveys, 40% of users report that improper installation contributes to malfunctioning equipment. Engaging staff in proper training can significantly reduce these errors.
Related Posts
-

Top 5 Benefits of Using Pneumatic Operated Valves in Industrial Applications
-

Top 10 Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Choices for Enhanced Automation Efficiency
-

Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Best Solenoid Valve Distributors for Your Needs
-

Discover the Ultimate Guide to SMC Cylinder Catalog: Enhance Your Automation Efficiency Today!
-

Top 7 Best Pneumatic Control Valves for Enhanced Industrial Performance
-

Top 10 Solenoid Valve Distributors: Find the Best Suppliers Near You
Get in Touch
570 Alden Road Unit #10, Markham Ontario Canada, L3R 8N5
Quick Links
Featured Products
Industries
