How to Choose the Right Pneumatic Solenoid for Your Automation Needs
Selecting the right pneumatic solenoid is a critical step in the design and functionality of automated systems. These components play a pivotal role in the control of air pressure and flow, directly influencing the efficiency and reliability of various applications. As automation technologies become increasingly sophisticated, understanding the specific requirements of your project—including factors like voltage, duty cycle, and response time—becomes essential in making an informed choice.
In the vast landscape of pneumatic solenoids, different models offer unique features designed to meet a variety of operational needs. From simple actuation to complex control systems, each pneumatic solenoid can have a significant impact on system performance. Therefore, it is important to not only consider the technical specifications but also the compatibility of the solenoid with other components in your automation setup. By thoroughly evaluating these aspects, you can ensure that the chosen pneumatic solenoid aligns with your automation goals, ultimately enhancing productivity and operational efficiency.

Understanding Pneumatic Solenoids and Their Applications
Pneumatic solenoids are vital components in various automation applications, acting as the interface between electrical control signals and mechanical movement. Understanding their functions, types, and applications can significantly enhance operational efficiency and reliability in industrial processes. According to a recent industry report from MarketsandMarkets, the global pneumatic automation market is projected to reach $41.4 billion by 2026, underscoring the rising demand for efficient actuators like pneumatic solenoids across sectors such as manufacturing, logistics, and automotive.
In many applications, such as automated assembly lines and robotic systems, pneumatic solenoids provide quick response times and robust actuation capabilities. They are widely used for controlling cylinders, valves, and various mechanisms that require precise movement. The versatility of pneumatic solenoids allows them to perform in harsh environments and under varying temperature conditions, making them ideal for industries like food and beverage, where hygiene and reliability are critical. According to a study by ResearchAndMarkets, the adoption of smart automation solutions incorporating pneumatic components is expected to grow by 15% annually, indicating a shift towards more sophisticated system integrations that enhance productivity and reduce downtime.
Furthermore, the choice of a pneumatic solenoid depends on specific factors such as operating pressure, response time, and the type of control required. Industries increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making to select the appropriate solenoid for their needs. By analyzing performance metrics and application requirements, companies can ensure they implement the most effective solutions that contribute to streamlined operations and increased overall productivity.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Pneumatic Solenoid

When selecting a pneumatic solenoid for automation applications, several key factors must be taken into account to ensure optimal functionality and reliability. First and foremost, consider the operating pressure and temperature range of your system. Pneumatic solenoids are designed to function within specific pressure and temperature limits, and choosing a solenoid that falls outside of these parameters can lead to performance issues or premature failure. Understanding the specific conditions of your environment will help in identifying the right solenoid that meets those requirements effectively.
Another crucial factor is the coil voltage compatibility. Pneumatic solenoids come with different coil voltages; selecting one that matches your control system is essential for proper operation. Additionally, it's important to evaluate the response time and flow rate of the solenoid. High-speed applications may require solenoids with rapid actuation speeds and adequate flow capacity to maintain efficiency. Assessing the electrical requirements, such as whether the system utilizes AC or DC voltage, will further guide the selection process. By carefully considering these factors, you can choose a pneumatic solenoid that aligns with your automation needs and enhances the overall performance of your systems.
Comparative Analysis of Different Types of Pneumatic Solenoids
When selecting a pneumatic solenoid for automation systems, it is crucial to understand the different types available and their specific applications. Pneumatic solenoids typically fall into two main categories: direct-acting and pilot-operated. Direct-acting solenoids are favored for their quick response times and ability to operate with low pressure, making them suitable for simple on/off applications. They generally have fewer components, which can enhance reliability and reduce maintenance needs.
On the other hand, pilot-operated solenoids utilize a smaller internal solenoid to control a larger valve, allowing them to handle higher flow rates and pressures with greater efficiency. They are often preferable for more complex systems where space is constrained or where substantial output is required. Understanding the requirements of your specific automation needs, such as flow rate, pressure tolerance, and response time, is essential in choosing between these types of solenoids. This comparative analysis can help streamline operations and improve overall system performance.
Assessing the Technical Specifications of Pneumatic Solenoids
When selecting a pneumatic solenoid for automation applications, it is crucial to assess various technical specifications to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Key factors include voltage, duty cycle, and response time, as these elements impact the solenoid's operation within a system. According to a report by the International Society of Automation, improper selection of solenoids can lead to a 12% decrease in system efficiency, emphasizing the importance of thorough evaluation.
One critical specification to consider is the voltage range. For instance, solenoids typically operate on either AC or DC voltages. AC solenoids are often preferred for their simpler control mechanisms, while DC options may offer faster response times. Additionally, the duty cycle—defined as the ratio of operating time to the total cycle time—should match your application requirements to avoid overheating and premature failure.
Tips: When assessing solenoids, always compare the flow rate and pressure ratings of different models. Ensure compatibility with your existing systems by checking dimensions and mounting configurations. Finally, consult performance charts and manufacturer data sheets to understand the trade-offs between response speed and power consumption, aligning these with your automation goals.
How to Choose the Right Pneumatic Solenoid for Your Automation Needs - Assessing the Technical Specifications of Pneumatic Solenoids
| Specification | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | Voltage required for activation | 24 VDC |
| Coil Resistance | Resistance of the solenoid coil | 50 Ohms |
| Flow Rate | Volume of air that can pass through | 15 l/min |
| Max Pressure | Maximum pressure that can be handled | 8 bar |
| Response Time | Time taken to respond to activation | 20 ms |
| Body Material | Material used for solenoid body | Aluminum |
| Mounting Type | Type of mounting available | DIN Rail |
Integration of Pneumatic Solenoids into Automation Systems
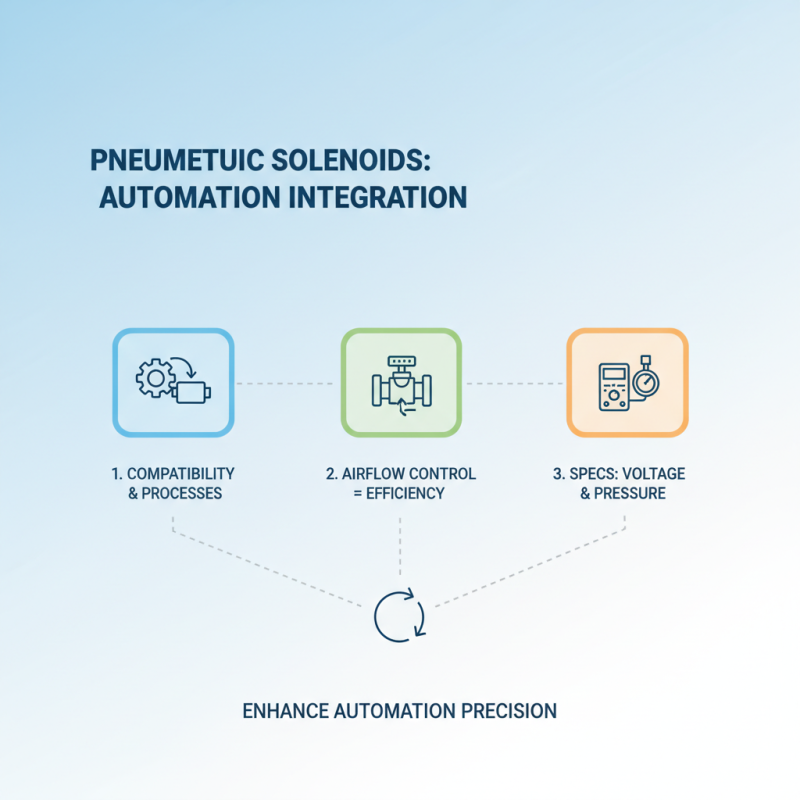
When integrating pneumatic solenoids into automation systems, it's crucial to ensure compatibility with existing components and processes. Pneumatic solenoids play an essential role in controlling the flow of air in automated systems, which can significantly enhance efficiency and precision. Consideration should be given to the specifications of the solenoid, such as its voltage ratings and operational pressure, as these factors determine its performance in the specific application.
**Tips:** Always verify the power requirements and pressure specifications before selecting a solenoid to avoid potential failures. Additionally, analyze the response times needed for your system; some applications may require faster actuation speeds than others.
Moreover, proper installation and integration are vital. Ensure that the solenoid is correctly mounted and that all connections are secure to prevent leaks and ensure optimal functionality. Utilize appropriate connectors and fittings that match your setup, as this can have a significant impact on operational reliability and maintenance.
**Tips:** Regularly check for wear and tear on solenoid components to prevent unexpected downtime. Implementing diagnostic features in your automation system can also help monitor solenoid performance, allowing for timely interventions if any issues arise.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Role of Pneumatic Solenoids in Modern Automation Systems
-

How to Choose the Right Pneumatic Air Cylinder for Your Industrial Applications
-

How to Choose the Right Pneumatic Air Cylinder for Your Application
-

Unlocking the Future: How Automation Solutions Are Transforming Everyday Life
-

Top 10 Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Choices for Enhanced Automation Efficiency
-
2025 Top 5 Machine Vision Systems Revolutionizing Industry Automation
Get in Touch
570 Alden Road Unit #10, Markham Ontario Canada, L3R 8N5
Quick Links
Featured Products
Industries
